Introducing pganalyze Query Advisor: Proactive Query Plan Optimization for Postgres
Postgres teams know the pain of one slow query snowballing into latency or downtime. Some have experimented with GenAI analysis, but it is too expensive to run continuously in the background. Others rely on general monitoring tools, but those cannot detect Postgres-specific patterns in query plans. What’s missing is a purpose-built, cost-effective solution that understands Postgres deeply and gives you actionable guidance.
At pganalyze we create purpose-built systems that address common Postgres challenges in production. Today, we’re excited to introduce pganalyze Query Advisor. It continuously analyzes EXPLAIN plans, detects problematic patterns, and provides clear query rewrites you can test and apply with confidence.
Postgres does not always pick the best execution plan, and figuring out why can take hours of manual EXPLAIN analysis. Query Advisor automates this work. It detects inefficient nested loops, poor index usage, and other anti-patterns, then suggests fixes before customers feel the impact.
What You Get With Query Advisor
When a query slows down in production, the troubleshooting process usually looks the same: someone notices a spike in latency, the team scrambles to reproduce the problem, EXPLAIN plans are pulled, and then hours are spent interpreting planner choices to figure out what went wrong. Even when the culprit is found, it takes more time to test potential rewrites and validate whether they actually help.
Query Advisor is built to optimize that entire cycle. Instead of waiting for a fire drill, it automatically reviews query plans as they come in, highlights problems, and helps you connect the dots to a tested fix. The result is less guesswork, fewer incident responses, and faster turnaround from problem to solution.
Behind the scenes, Query Advisor continuously analyzes EXPLAIN plans in the background. This means you can detect problematic queries before they reach the point of slowing down customers. Instead of relying on reactive debugging, your team has a proactive safety net watching for inefficient patterns.
When Query Advisor finds something, it doesn’t just raise a vague alert. Notifications are sent to Slack or through an API, pointing directly to the issue and linking to a concrete rewrite suggestion. The right person on the team gets actionable guidance, not just a warning that something is wrong.
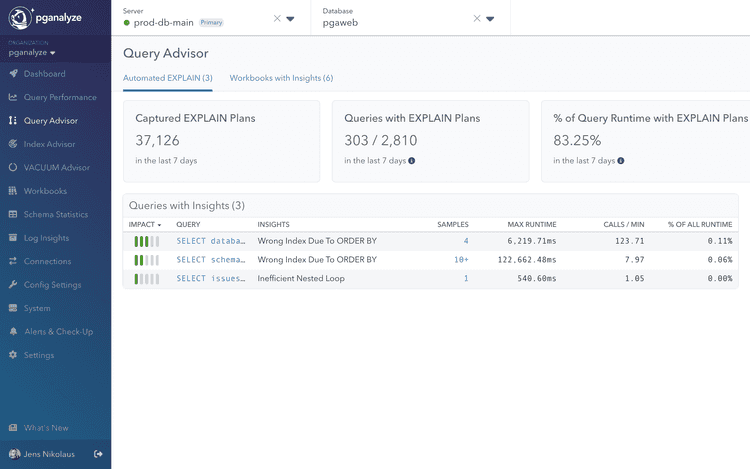
Query Advisor automatically surfaces insights from captured EXPLAIN plans.
Examples of Query Advisor in Action
Inefficient Nested Loops
Nested loop joins can be fast when Postgres loops over only a few rows. But when the planner underestimates row counts, it may scan the same table thousands of times unexpectedly.
Query Advisor detects when this pattern appears in your plans. For example:
SELECT o.*, c.customer_name
FROM orders o
JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.id
WHERE o.store_id = 'sf-union-square'
AND c.zipcode = 94108
AND c.city = 'San Francisco';If Postgres expects only a handful of rows to match in the customers table, it might choose a nested loop that first retrieves all customers with the given Zipcode and City, and then iterates over the orders table for each customer. But if the actual workload includes tens of thousands of matching customers, the orders table is scanned repeatedly. Query Advisor identifies this mismatch and suggests a rewrite that forces Postgres to filter first and then join more efficiently:
WITH filtered_orders AS MATERIALIZED (
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE store_id = 'sf-union-square'
)
SELECT o.*, c.customer_name
FROM filtered_orders o
JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.id
WHERE c.zipcode = 94108 AND c.city = 'San Francisco';Wrong Index Choice With ORDER BY + LIMIT
Another common pitfall appears when Postgres prioritizes the sort order requested by an ORDER BY clause, over filtering supporting a WHERE clause. Postgres may use an index to satisfy sort order but filter afterwards, scanning millions of rows to return a handful of results.
SELECT * FROM large_table
WHERE database_id = 123
ORDER BY created_at DESC
LIMIT 50;Postgres might choose the created_at index for sorting, which leads to wasted work. Query Advisor flags this pattern and suggests a simple workaround that changes planner behavior:
SELECT * FROM large_table
WHERE database_id = 123
ORDER BY created_at + 0 DESC
LIMIT 50;
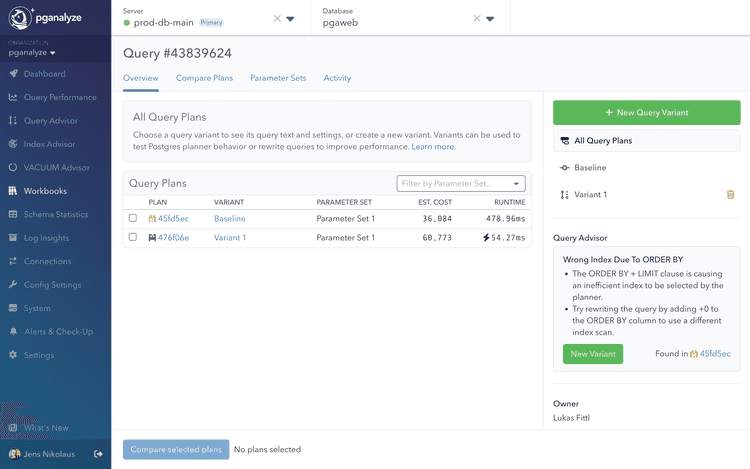
Detected issues are visible directly in Workbooks, linked from Query Advisor.
Looking Ahead
At launch we are focused on specific insights on common plan problems. In our early access program, we’ve seen over half of customers participating having insights on unexpected slow query plans that Query Advisor can detect and fix using a query rewrite.
However, sometimes there are alternate ways to resolve bad query plans like this—for example, in the earlier Nested Loop case, you could create extended statistics on the customers table to help Postgres estimate better, and we are planning to introduce CREATE STATISTICS recommendations into Query Advisor at a future point.
We are also looking at expanding Query Advisor to other common causes of wrong index use, for example situations where OR can be rewritten as a UNION, and more. Your feedback on additional logic to add is welcome! Query Advisor is built to encode the knowledge of Postgres experts collected and shared with the community over the years, and our goal is for it to reduce repetitive triage of common planner problems.
Getting Started With Query Advisor
To begin with detecting plan problems automatically, install the pganalyze collector and ensure EXPLAIN plans are being captured with auto_explain. Query Advisor requires use of the auto_explain extension with log_analyze enabled for accurate row counts, and log_format to be set to json for its analysis to run. See the recommended settings in the pganalyze auto_explain installation guide for your platform.
When auto_explain is configured correctly, Query Advisor automatically analyzes incoming plans in the background.
You can view detected insights in the Query Advisor landing page, issue detail pages, and directly in Workbooks and query detail views. To make sure your team hears about new findings quickly, you can also configure Slack alerts for Query Advisor.
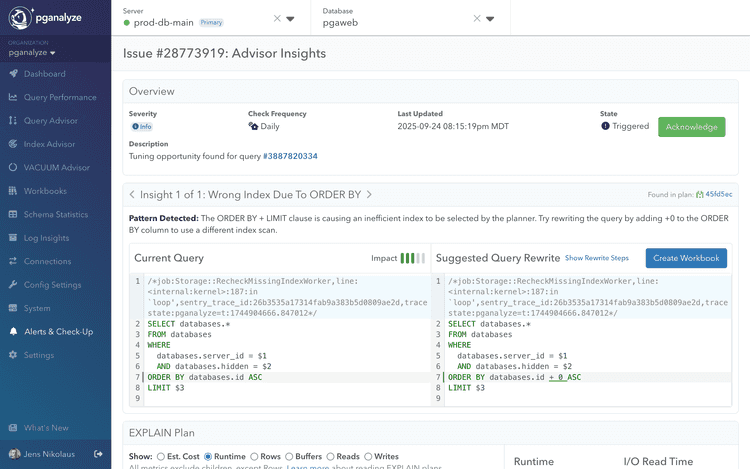
Insight detected: Wrong Index Due to ORDER BY, with suggested rewrite preview.
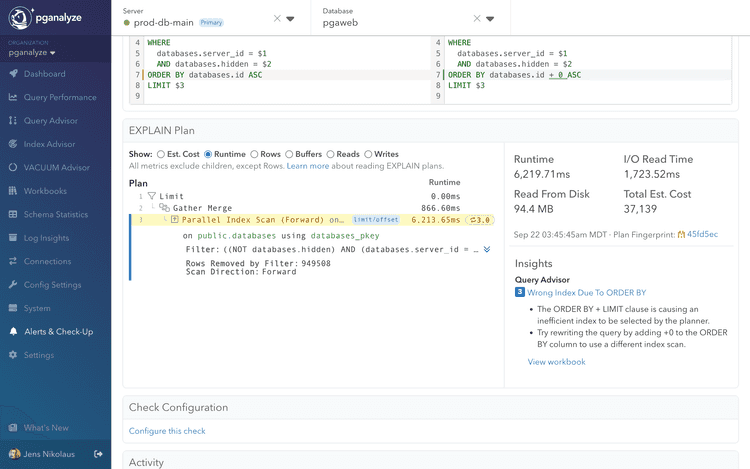
The EXPLAIN plan view highlights the inefficient index scan and suggests a rewrite.
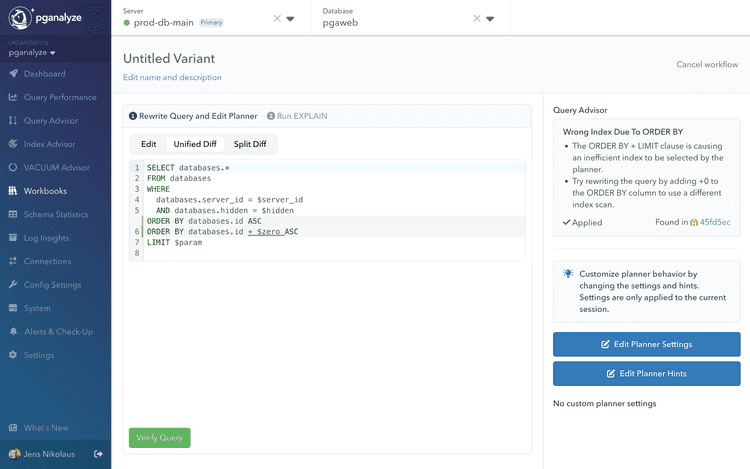
Easily apply insights and prepare them for testing.
Conclusion
pganalyze Query Advisor turns a large stream of collected Postgres query plans into actionable optimization recommendations. By automatically detecting common anti-patterns like inefficient nested loops and poor index choices on ORDER BY queries, it helps you prevent downtime, improve performance, and deploy fixes with confidence.
Query Advisor is available starting today for customers on current pganalyze Scale and pganalyze Enterprise Cloud plans, followed by a pganalyze Enterprise Server release in a few weeks.
This is just the beginning. Query Advisor will continue to expand its library of insights, but it is already making a measurable difference for teams running Postgres in production. Get started today!





